Have you ever wondered about logarithmic functions and their graphs? They may sound intimidating, but they’re actually quite fascinating once you understand them. Let’s take a closer look at how logarithmic functions work and how their graphs appear.
Logarithmic functions are the inverse of exponential functions. Instead of growing rapidly like exponential functions, logarithmic functions grow at a slower rate. They are commonly used in various fields such as science, engineering, and finance to model data that changes exponentially.
Logarithmic Functions And Their Graphs
Logarithmic Functions And Their Graphs
When graphing a logarithmic function, the x-axis represents the input or the base, while the y-axis represents the output or the exponent. The graph of a logarithmic function looks like a curve that approaches but never touches the x-axis.
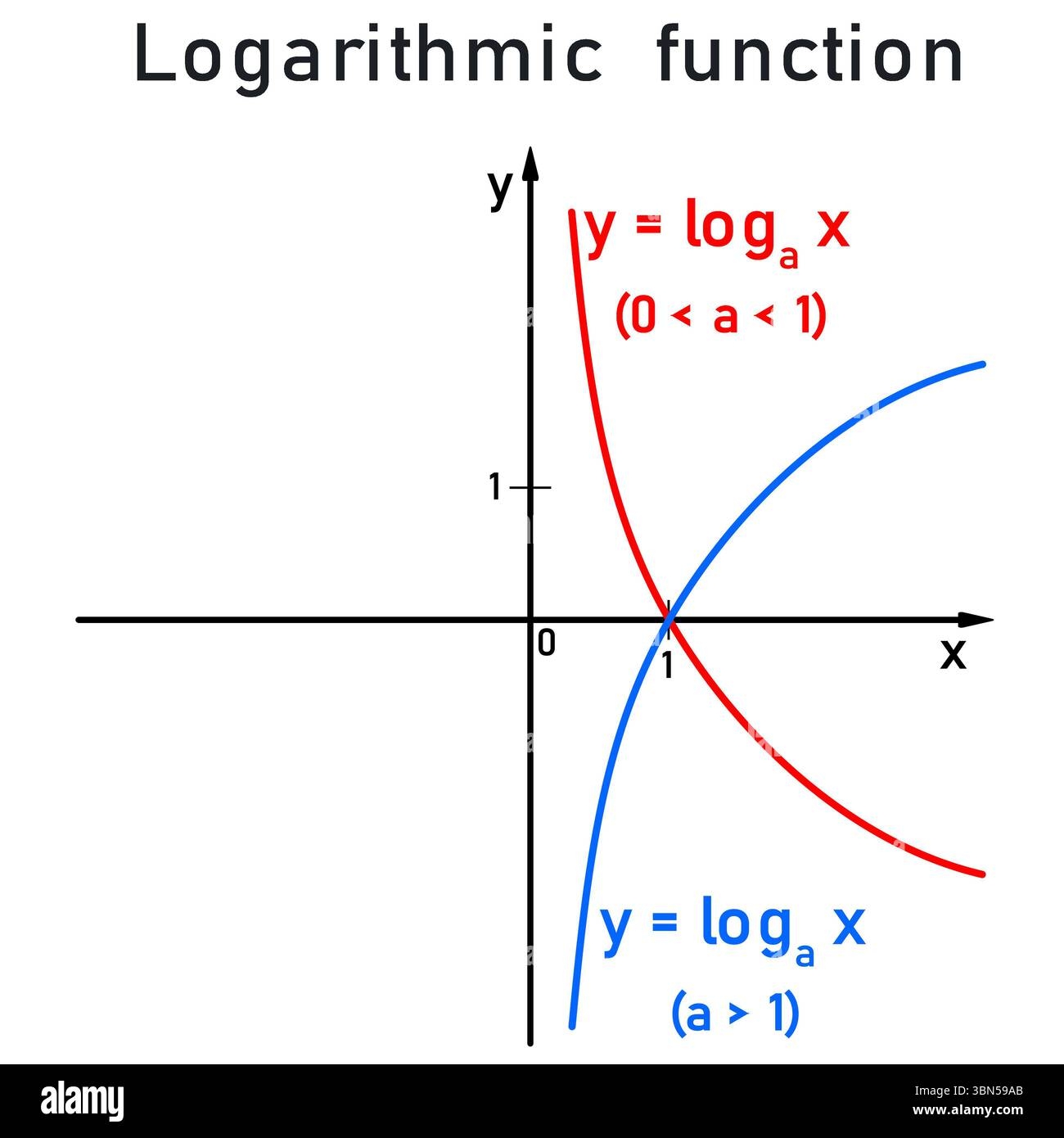
The shape of a logarithmic graph depends on the base of the logarithm. For example, a logarithmic function with a base greater than 1 will have a graph that increases as it moves to the right, while a base between 0 and 1 will have a graph that decreases as it moves to the right.
Understanding logarithmic functions and their graphs can help you analyze data more effectively and make informed decisions based on trends and patterns. Whether you’re studying math, science, or any other subject, having a solid grasp of logarithmic functions can be beneficial.
In conclusion, logarithmic functions and their graphs may seem complex at first, but with a little practice and patience, you can master them. By learning how to interpret and manipulate logarithmic functions, you can gain valuable insights into the world around you and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Vector Set Of Graphs With 12 Basic Functions Linear Constant Absolute Value Greatest Integer Logarithmic Exponential Reciprocal Square Root Goniometric Quadratic Cubing Logistic Function Stock Vector Adobe Stock
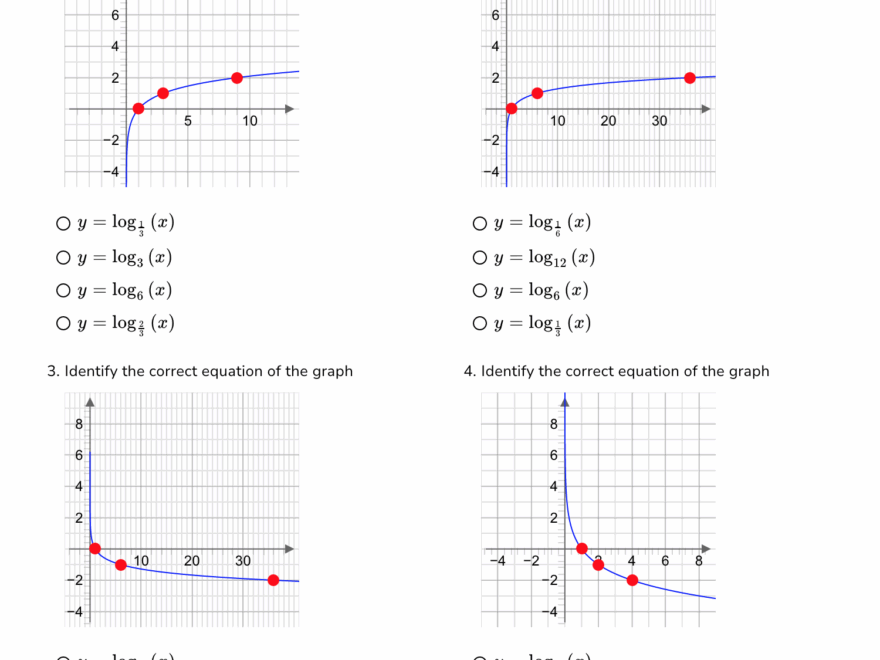
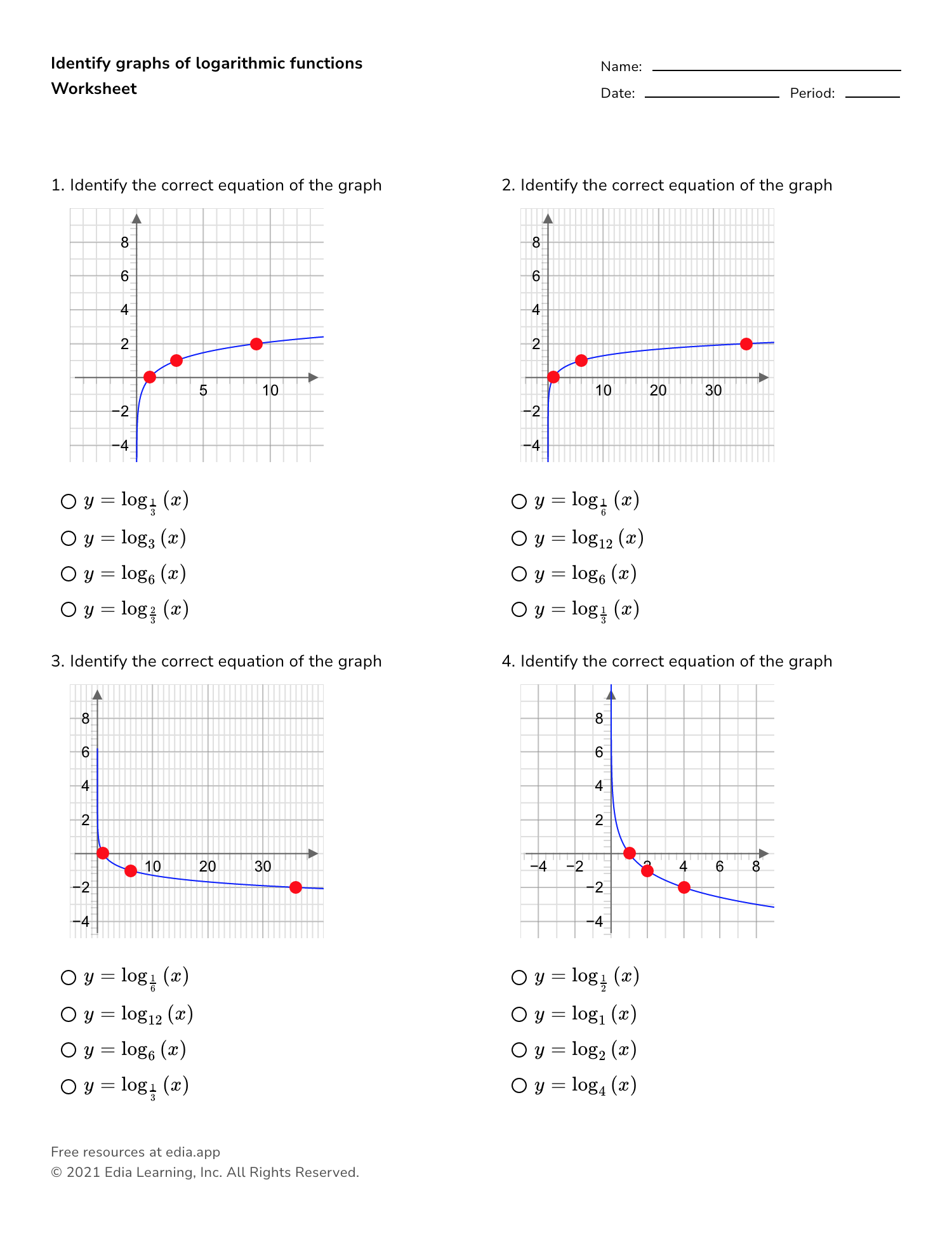
Identify Graphs Of Logarithmic Functions Worksheet