Thermistors are small, sensitive components that can change resistance with temperature. This change in resistance can be plotted on a graph, known as an IV graph. Understanding the IV graph of a thermistor is crucial for various applications.
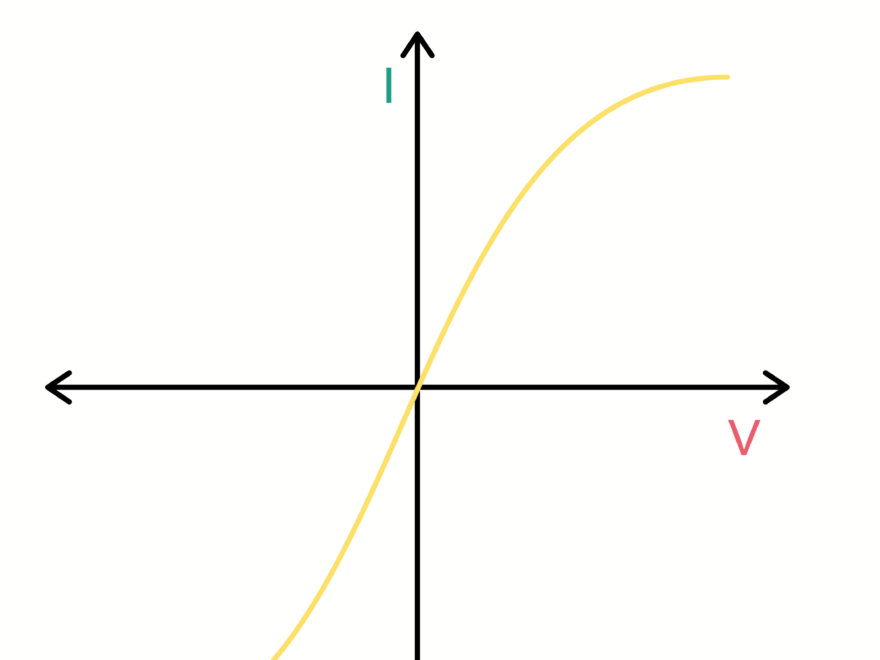
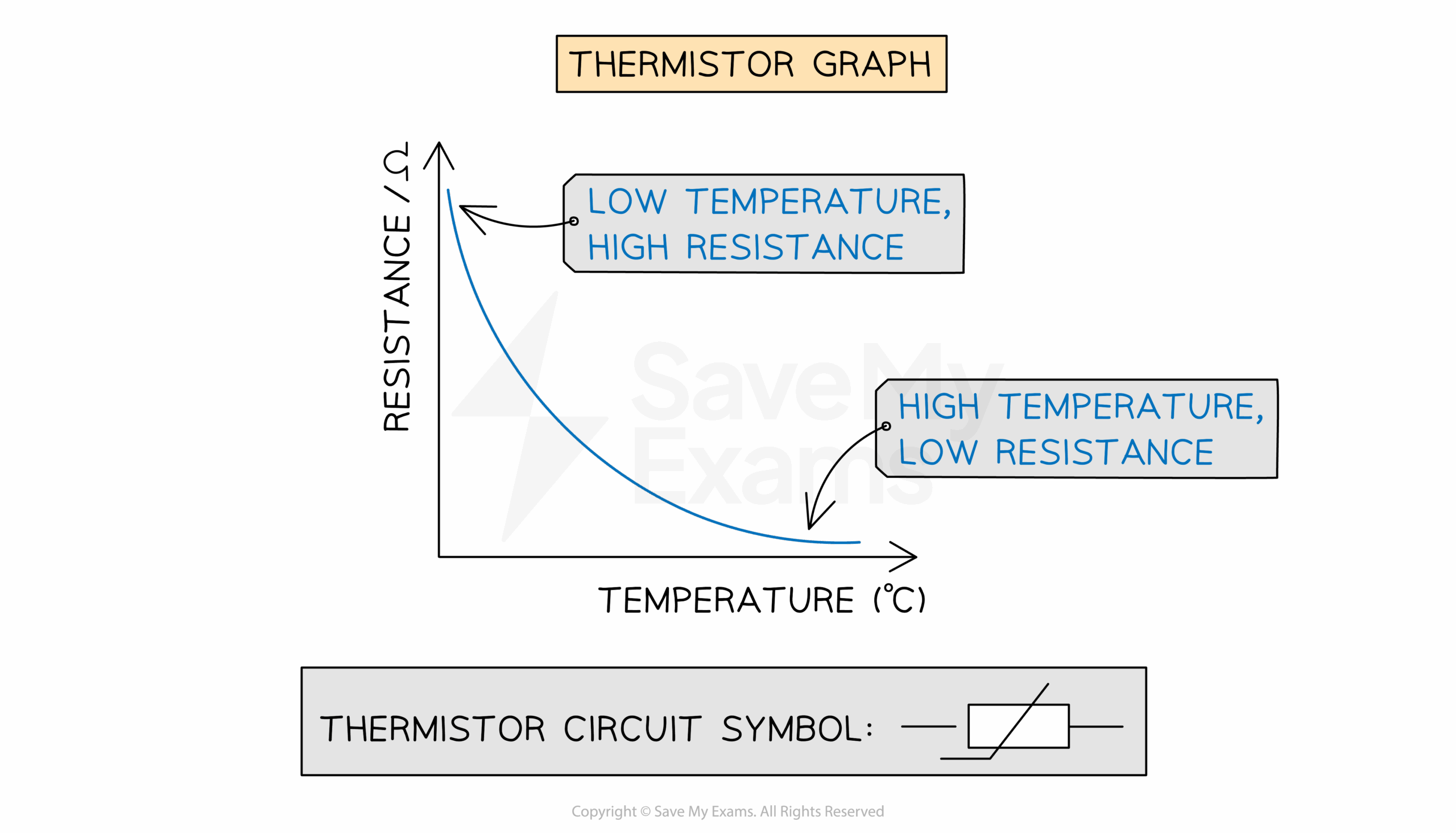
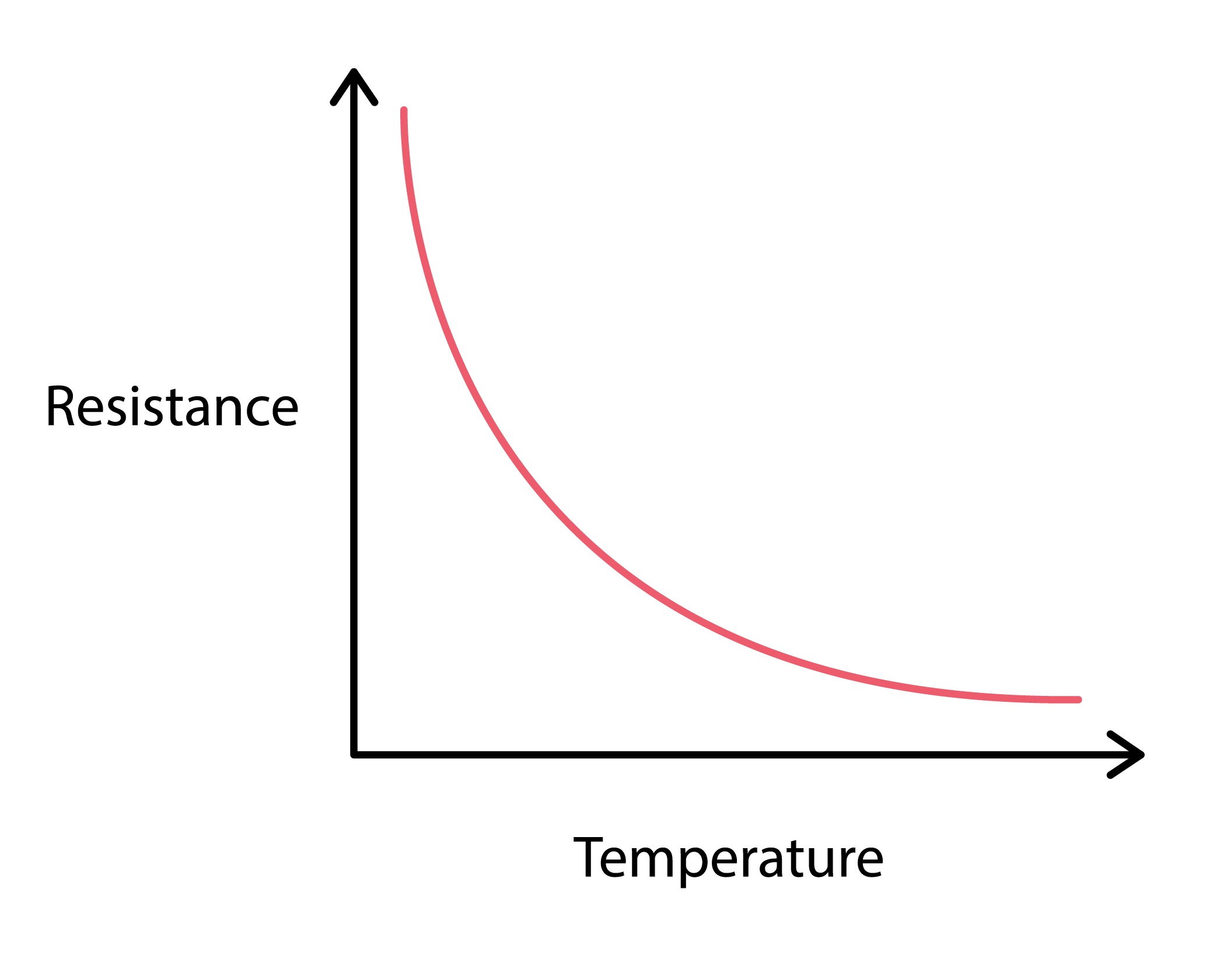
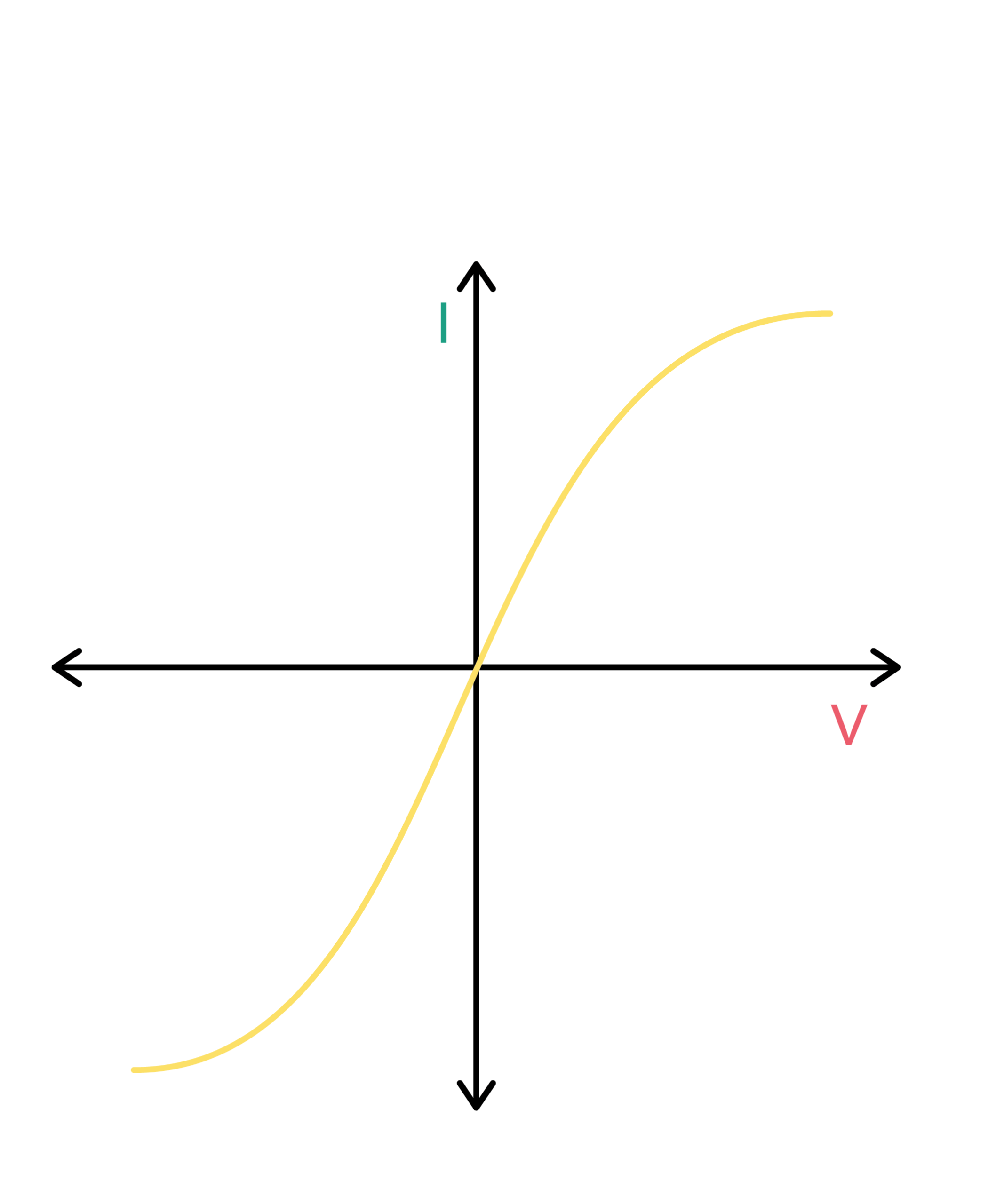
When looking at the IV graph of a thermistor, you’ll notice a non-linear relationship between resistance and temperature. As the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases exponentially. This unique characteristic makes thermistors ideal for temperature sensing and control.
Iv Graph Of Thermistor
The IV Graph of Thermistor
The IV graph of a thermistor typically consists of a curve that shows how the resistance changes with temperature. At lower temperatures, the resistance is high, but as the temperature rises, the resistance decreases rapidly. This behavior is what makes thermistors so valuable in temperature-sensitive applications.
By analyzing the IV graph of a thermistor, engineers and researchers can determine the temperature accurately and make necessary adjustments in systems where temperature control is critical. This information is vital in industries such as automotive, medical, and HVAC, where precise temperature monitoring is essential.
It’s important to note that the IV graph of a thermistor can vary depending on the type of thermistor used. There are two main types of thermistors: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) and PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient). Each type exhibits a different IV graph, so it’s essential to choose the right thermistor for your specific application.
In conclusion, understanding the IV graph of a thermistor is key to utilizing these components effectively in temperature-sensitive applications. By interpreting the curve on the graph, you can accurately measure and control temperature, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in various systems.
I V Characteristics Physics Explanation Exercises Evulpo
I V Characteristics Physics Explanation Exercises Evulpo