Understanding polar coordinates and basic graphs can seem daunting at first, but with a little guidance, it can become second nature. These concepts are essential in mathematics and physics, and mastering them can open up a world of possibilities.
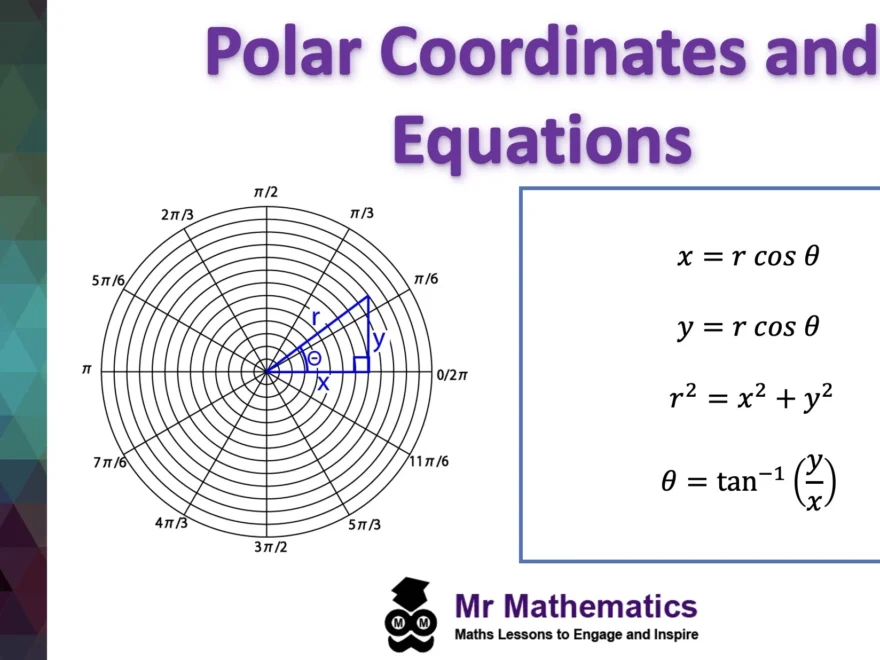
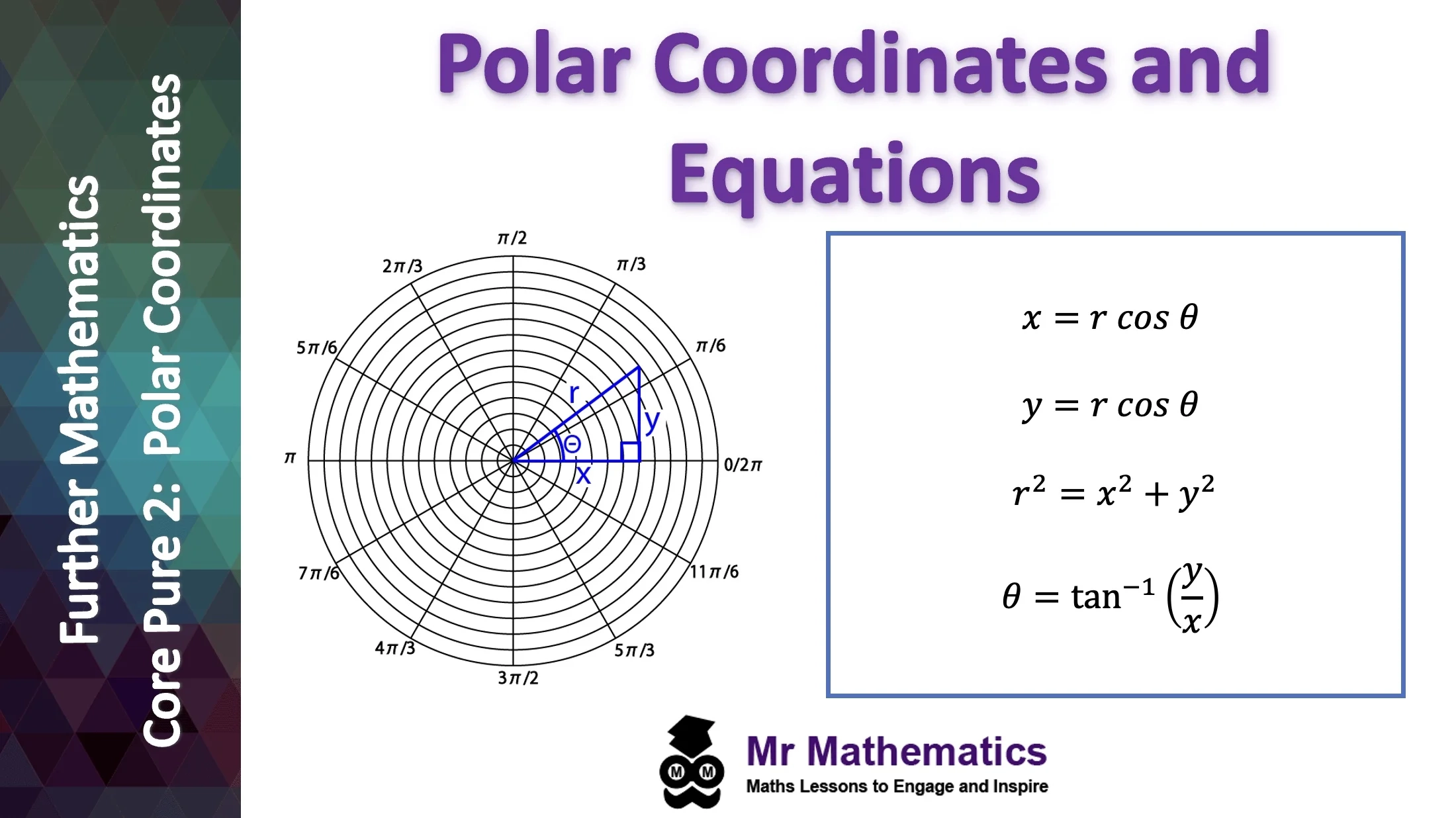
When we talk about polar coordinates, we are referring to a system where each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a fixed point and an angle from a fixed direction. This differs from the Cartesian coordinates we are more familiar with, which use x and y axes.
Polar Coordinates And Basic Graphs
Polar Coordinates And Basic Graphs
In polar coordinates, the distance from the fixed point is called the radial coordinate or radius, denoted by ‘r,’ and the angle from the fixed direction is called the angular coordinate or azimuthal angle, denoted by ‘θ.’ Together, these two values uniquely define a point on the plane.
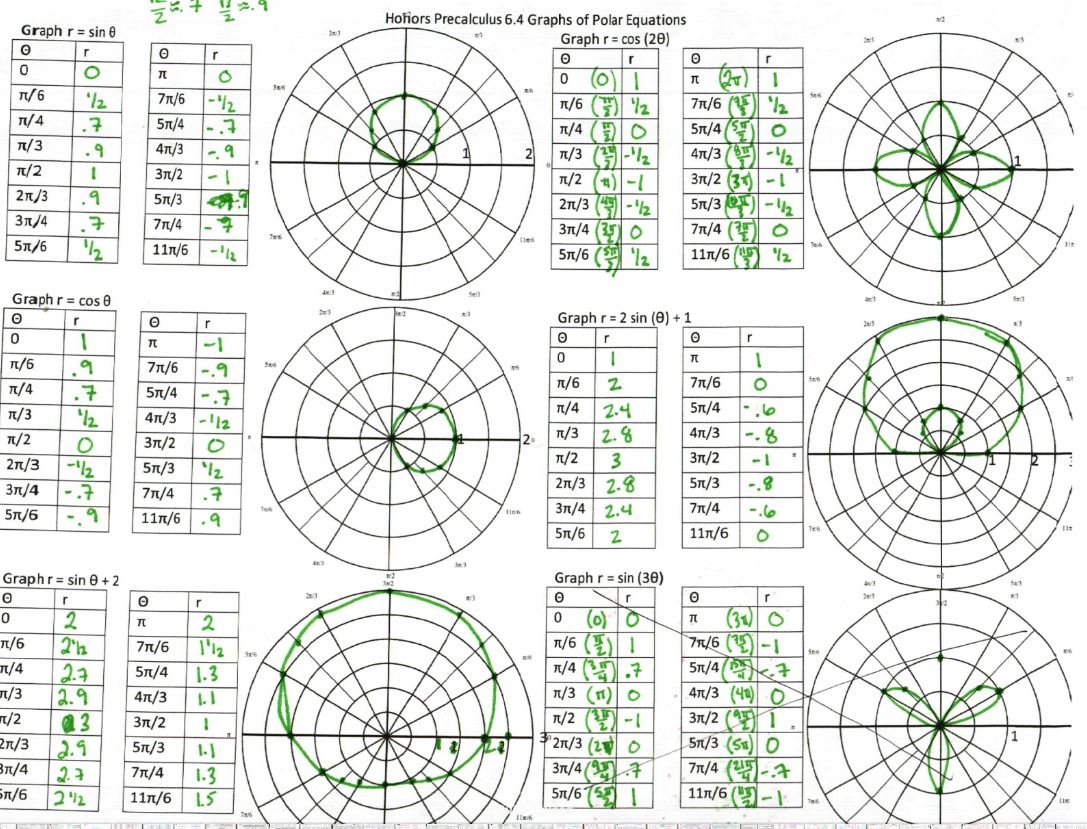
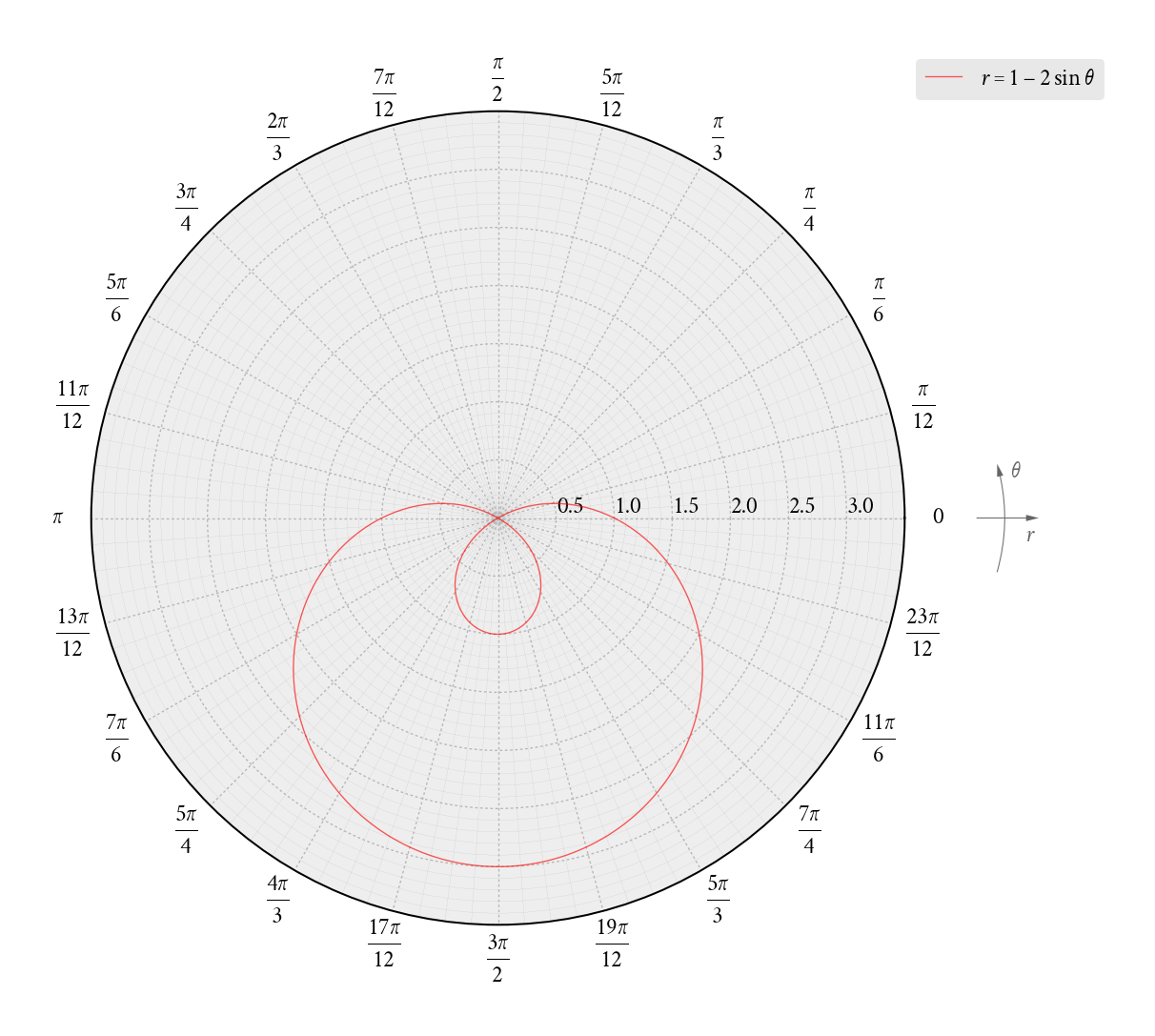
Basic graphs in polar coordinates include circles, lines, and spirals. Circles in polar coordinates are given by r = a, where ‘a’ is the radius of the circle. Lines are represented by equations of the form r = a / cos(θ – α), where ‘a’ is the distance of the line from the origin, and ‘α’ is the angle the line makes with the x-axis.
One of the most famous polar graphs is the Archimedean spiral, given by r = a + bθ, where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constants. This spiral increases in radius as the angle increases, creating a visually appealing graph that is used in various applications.
Mastering polar coordinates and basic graphs opens up a world of possibilities in mathematics, physics, and engineering. From analyzing complex systems to understanding the nature of motion, these concepts are fundamental to many fields of study. So, grab a pen and paper, and start exploring the wonders of polar coordinates today!
Trigonometry Negative Radial Coordinates In Polar Plots Mathematics Stack Exchange
Polar Coordinates Archives Mr Mathematics